一、项目的创建
1、创建方式
(1)使用官方的脚手架
1
| npx create-react-app <projectname>
|
只做 React 基本的搭建和构建,没有路由和状态管理,项目使用 Webpack 构建
(2)使用一些市场上的集成脚手架
官方脚手架提供的项目模板非常简单,因此也有很多集成的脚手架,比如:umi
这类脚手架创建的项目会集成很多功能,比如:路由、mock
2、两个核心库
(1)React
创建一个 React 对象,提供 React 的各个功能
(2)React-dom
提供一些 DOM 操作方法,用于把 React 创建出来的 React 对象 挂载到真正的 html DOM 中,或者从 HTML DOM 中卸载,作用类似于 Vue 的 mount
二、React 组件 和 JSX
1、组件分类
(1)函数组件
1
2
3
| function Hello() {
return <div>hello</div>
}
|
class 组件(老版本)
1
2
3
4
5
| class Hello extends React.Component {
render () {
return <div>hello</div>
}
}
|
2、JSX 特点
(1)直接在 JS 中混用
React 项目利用 Babel 做了对 JS 的编译,所以能直接在 JS 里写 JSX
(2)写法接近 JS
JSX 几乎和 JS 一样,不同点在于,可以在 JS 里写 HTML,且写在 JS 里的 HTML 最后会被编译成一个 JS 对象,也可以用 React 自带 createElement 创建这个对象
1
2
3
4
| function FnHello() {
return React.createElement("div", [], "Hello")
}
|
3、JSX 里面渲染不同内容的区别
(1)字符串、数字:直接渲染
(2)对象:只能渲染 element 对象,否则会报错
(3)数组:把数组中的每一项单独渲染
(4)表达式:运行表达式
(5)方法:无法渲染
(6)布尔值,undifined, null:不渲染
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| import React from 'react';
function App() {
function FnHello() {
return React.createElement("div", [], "Hello")
}
class ClassHello extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
}
render() {
return <div>hello class</div>
}
}
console.log("FnHello", FnHello)
console.log("<FnHello/>", <FnHello/>)
let eleObj = FnHello()
let com1 = <ClassHello></ClassHello>
let obj = { a: 123 }
let arr = [com1, 5, 'abc']
return (
<div className="App">
<FnHello></FnHello>
<ClassHello></ClassHello>
-------
{eleObj}
{com1}
-------
{"Hello Str"}
{123}
{/* {obj} 报错 */}
{/* {FnHello} 报错 */}
{arr}
{1+2+3+4}
{true?<FnHello></FnHello>:'123'}
{/* {false} 不展示 */}
{/* {undefined} 不展示 */}
{/* {null} 不展示 */}
</div>
);
}
export default App;
|
三、React 的时事件绑定
1、规则模式
(1)类似于原生,on+方法名(首字母大写,为了和原生区分)
(2)一定要赋值给事件一个方法
2、特别注意的问题
(1)不作处理的情况下,this 会指向 undefined
(2)事件绑定的必须是一个方法,不要直接调用方法,否则只会在页面初次渲染时执行
3、事件绑定其他操作
(1)传递参数
(2)获取事件对象
(3)阻止默认行为,冒泡等
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
| import React from 'react';
class App extends React.Component {
f1() {
console.log("this", this)
}
f2 = () => {
console.log("this", this)
}
f3(a, b) {
console.log("a + b =", a + b)
}
f4 = (a, b) => {
console.log("a + b =", a + b)
}
f5(a) {
console.log("a", a)
}
f6(a, b, e) {
console.log("e", e)
e.stopPropagation();
e.preventDefault();
}
render() {
return <div className="App">
<div onClick={() => {
console.log(1)
}}>123</div>
<div onClick={this.f1.bind(this)}>456</div>
<div onClick={this.f2}>789</div>
{/* 不能传方法的调用 */}
<div onClick={this.f2()}>error</div>
{/* 箭头函数改变 this 指向 */}
<div onClick={() => {
console.log("this", this)
}}>匿名1</div>
{/* 普通函数不行 */}
<div onClick={function () {
console.log("this", this)
}}>匿名2</div>
{/* 事件传参 */}
{/* 1、普通函数.bind() + 普通函数 */}
<div onClick={this.f3.bind(this, 1, 2)}>传参1</div>
{/* 2、箭头函数 + 箭头函数 */}
<div onClick={() => this.f4(1, 2)}>传参2</div>
{/* 获取事件对象 */}
{/* 1、不传参 */}
<div onClick={this.f5.bind(this)}>事件1</div>
{/* 2、传参 */}
<div onClick={this.f6.bind(this, 1, 2)}>事件2</div>
</div>
}
}
export default App;
|
四、React 中的响应式数据
1、类组件响应式数据
响应式数据定义在类的 state 属性中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| class ClassState extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
a: 123
}
}
}
|
2、React 响应式原理
(1)React 不能像 Vue 一样直接修改触发更新
(2)React 修改能改值,但无法触发更新,因为 React 不像 Vue 监听了 get 和 set,而是在调用 setState 时调用 React 的更新操作
3、setState 关键点
(1)通过浅合并来修改数据
(2)调用 setState 方法会触发更新,修改 state 不会触发更新
(3)setState 方法是异步的,如果要获取修改后的值,需要在 setState 的第二个参数里获取
(4)setState 方法多次修改,会合并为一次,统一更新
(5)setState 返回会触发更新,不管是否有修改,这导致:重复修改为相同的值也会让组件更新
(6)一定不要在 render 里直接 setState
4、PureComponent 下对于对象和数组的修改
PureComponent 会根据 state 是否改变来决定是否更新,而对于对象、数组这种引用类型判断是否改变的原理是看内存地址,而不是内容
因此在 PureComponent 下修改对象和数组,需要声明一个新对象赋值。所以一般不直接操作原对象,而是先拷贝一份,再进行操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
| import React from 'react';
class App extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
a: 0,
b: 1,
c: {
c1: 123,
c2: 999
},
arr: [1, 2, 3]
}
addA = () => {
this.setState({
a: this.state.a + 1
})
this.setState({
a: this.state.a + 1
})
console.log("this.state.a", this.state.a)
}
merge = () => {
this.setState({
a: 1,
b: 2,
c: {
...this.state.c,
c1: 9
}
}, () => {
console.log("this.state0", this.state)
})
console.log("this.state1", this.state)
}
refresh = () => {
this.setState({
a: 1
})
this.setState({
b: 2
})
}
addArr = () => {
let arr_ = [...this.state.arr]
arr_.push(4)
this.setState({
arr: arr_
}, () => {
console.log("this.state.arr", this.state.arr)
})
this.setState({
c: {
...this.state.c,
c1: 8888
}
}, () => {
console.log("this.state.c", this.state.c)
})
}
render() {
console.log(123)
return <div className="App">
{this.state.a}
<button onClick={() => this.addA()}>加1</button>
<button onClick={() => this.merge()}>合并</button>
<button onClick={() => this.refresh()}>更新</button>
{this.state.arr}
<button onClick={() => this.addArr()}>数组增加</button>
</div>
}
}
export default App;
|
五、条件渲染和列表循环
React 没有 Vue 一样的指令,一切操作本质上是通过运算生成不同的内容,再渲染得到不同的页面
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| import React from 'react';
class App extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
show: true,
originArr: [1, 2, 3]
}
f1() {
if(this.state.show) {
return <div>div1</div>
}
return ""
}
getArr() {
let newArr = []
this.state.originArr.forEach((item) => {
newArr.push(<div>{item}</div>)
})
console.log('newArr', newArr)
return newArr
}
addData = () => {
let _arr = [...this.state.originArr]
_arr.push(Math.random() * 10)
this.setState({
originArr: _arr
})
}
render() {
return <div className="App">
<div>条件渲染</div>
{/* {this.state.show ? <div>div1</div>: ""} */}
{this.f1()}
<button onClick={() => {
this.setState({
show: !this.state.show
})
}}>{this.state.show ? "隐藏" : "显示"}</button>
<div>列表渲染</div>
{/* { this.getArr() } */}
{
this.state.originArr.map((item) => {
return <div key={item}>{item}</div>
})
}
<button onClick={() => this.addData()}>添加</button>
</div>
}
}
export default App;
|
六、表单绑定
React 中很多思路都是按原生的操作去做的,表单绑定也是如此
原生表单获取表单输入值,可以通过监听 input、change 等事件,然后获取 e.target.value
如果要设置表单的值,通常设置 value 属性,如果是选择框则是 checked 属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| import React from 'react';
class App extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
inputValue: "",
checkedArr: ["c2"]
}
handleChecked = (e) => {
let arr = [...this.state.checkedArr]
if(e.target.checked) {
arr.push(e.target.value)
}
else {
arr.splice(arr.indexOf(e.target.value), 1)
}
this.setState({
checkedArr: arr
})
}
render() {
return <div className="App">
{/* <input onBlur={} /> */}
{/* <input onChange={} /> */}
<input value={this.state.inputValue} onInput={(e) => {
this.setState({
inputValue: e.target.value
})
}} />
{ this.state.inputValue }
{/* checkbox */}
<input checked={this.state.checkedArr.indexOf("c1")!==-1} type="checkbox" value="c1" name="choose" onChange={this.handleChecked} />
<input checked={this.state.checkedArr.indexOf("c2")!==-1} type="checkbox" value="c2" name="choose" onChange={this.handleChecked} />
<input checked={this.state.checkedArr.indexOf("c3")!==-1} type="checkbox" value="c3" name="choose" onChange={this.handleChecked} />
{ this.state.checkedArr }
</div>
}
}
export default App;
|
七、props 和组件间传值、插槽
props 是 React 中的核心,一切写在组件上的属性和子节点都被划为 props
React 父子传值,插槽全都基于 props,不像 Vue 有事件监听、emit、专门的插槽 这类东西
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
import React from 'react';
import Son from './Son';
class App extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
msg: "app message"
}
changeMsg = (sonMsg) => {
console.log("sonMsg", sonMsg)
this.setState({
msg: sonMsg
})
}
render() {
return <div className="App">
I'm App.
<br></br>
{/* 具名插槽 */}
{/* 在插槽中显示子组件内容 */}
{/* <Son msg={this.state.msg} a={<div>I'm slot2</div>} scopeslot={(scope) => {
return <div>scope: {scope}</div>
}}>
<div>I'm slot</div>
</Son> */}
<Son msg={this.state.msg} changeMsg={this.changeMsg}>
</Son>
</div>
}
}
export default App;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
|
import React from "react"
import proptypes from "proptypes"
class Son extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
sonMsg: "son message"
}
render() {
return <div>
{this.props.msg}
<button onClick={() => this.props.changeMsg("hello, father")}>修改</button>
</div>
}
}
Son.propTypes = {
msg: proptypes.string
}
Son.defaultProps = {
msg: "default"
}
export default Son;
|
八、React 样式设置
1、class 类名设置
(1)必须写为 className
(2)类名和样式写在 css 文件里
(3)必须接受一个字符串
2、style 内联
不能像原生一样写成字符串,必须写成对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
import './App.css';
import React from 'react';
import Son from './Son';
class App extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
msg: "app message"
}
render() {
return <div>
<div className="father" style={
{
background: "yellow",
fontSize: "25px"
}
}>father</div>
<Son></Son>
</div>
}
}
export default App;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
import React from "react"
import proptypes from "proptypes"
import sonStyle from "./Son.module.css"
import classnames from "classnames/bind"
let bindClassnames = classnames.bind(sonStyle)
let str = classnames({
son: true,
son1: true
})
console.log("str", str)
class Son extends React.PureComponent {
state = {
sonMsg: "son message",
hasSon1: false
}
render() {
return <div>
{/* 取出新的 class 名 */}
<div className={sonStyle.son + " " + sonStyle.son1}>son1</div>
{/* classnames 库 */}
{/* 非模块化 */}
<div className={classnames({
son: true,
son1: this.state.hasSon1
})}>son2</div>
{/* 模块化 */}
<div className={bindClassnames({
son: true,
son1: this.state.hasSon1
})}>son3</div>
</div>
}
}
Son.propTypes = {
msg: proptypes.string
}
Son.defaultProps = {
msg: "default"
}
export default Son;
|
1
2
3
4
|
.father {
color: red
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
.son {
color: blue
}
.son1 {
background-color: bisque;
}
|
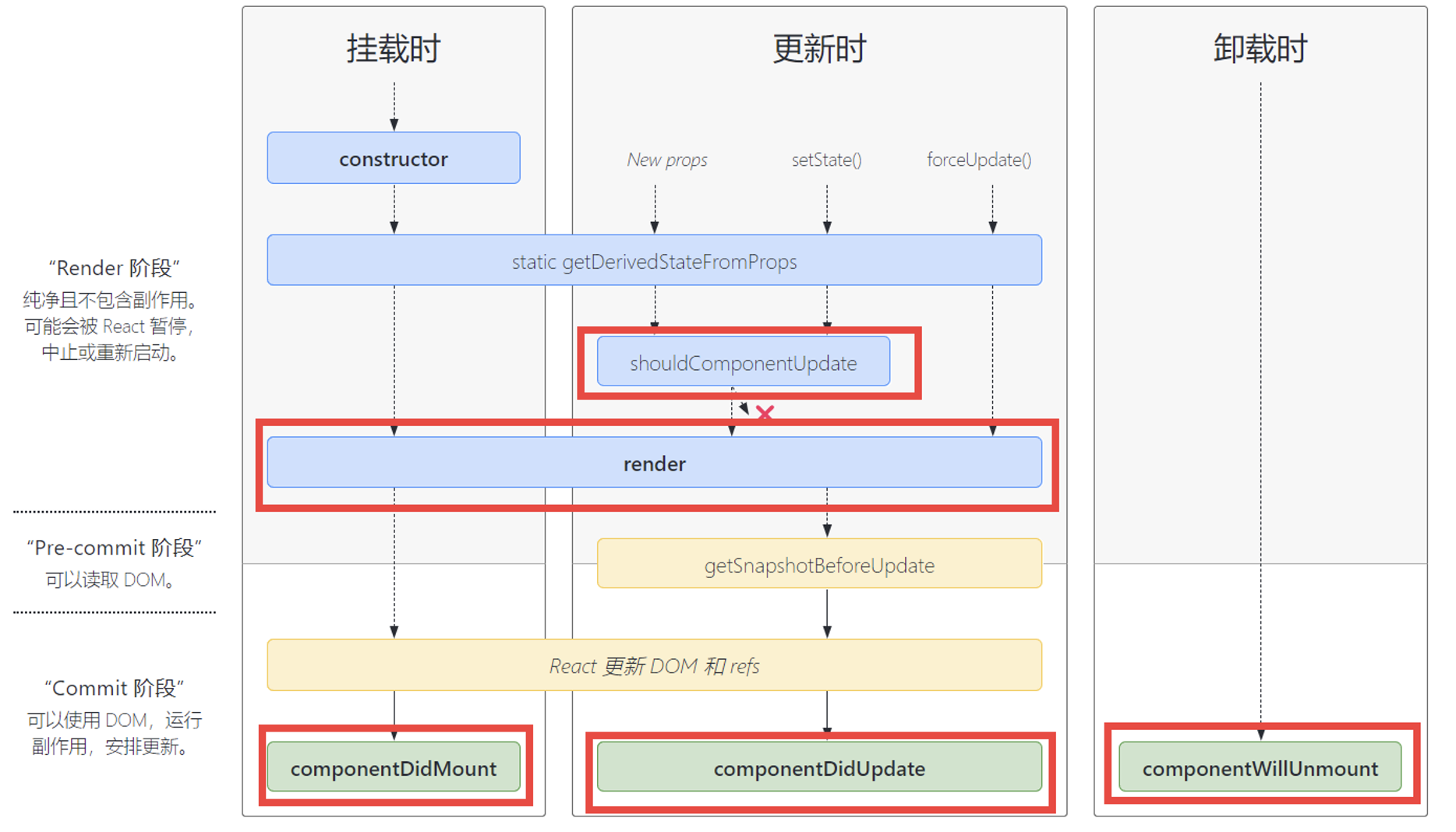
九、React 生命周期
1、生命周期图示

2、严格模式
严格模式只在开发模式下生效,生产上线时会去除,作用如下:
(1)检测危险操作(比如:使用已经废弃 api 和不推荐的 api)
(2)把生命周期执行两次,来检测额外副作用(比如:render)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>
);
|
3、React 和 Vue 更新
(1)Vue
Vue 是在 get 和 set 里触发更新,在 get 部分会进行依赖收集的操作
在更改数据后,只会更新用到该数据的地方,做到最小的更新范围
(2)React
React 的更新是调用方法时触发的,没有依赖收集的过程
所以会更新整个组件树、同时更新子组件,即使更新的数据和子组件没有关系
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
|
import './App.css';
import React from 'react';
import Son from './Son';
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
msg: "app message"
}
console.log("constructor")
}
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {
console.log("derived")
console.log("derived-props", props)
console.log("derived-state", state)
return null
}
shouldComponentUpdate(props, state) {
console.log("shouldUpdate")
console.log("shouldUpdate-this.state 修改前", this.state)
console.log("shouldUpdate-state 修改后", state)
for(let item in this.state) {
if(this.state[item] != state[item]) {
return true
}
}
return false
}
render() {
console.log("render")
return <div>
<div className="father">
<div>{this.state.msg}</div>
<button onClick={() => {
this.setState({
msg: "hello"
})
}}>修改msg</button>
<Son></Son>
</div>
</div>
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log("didMount")
}
componentDidUpdate() {
console.log("didUpdate")
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log("willUnmount")
}
}
export default App;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
import React from "react"
import proptypes from "proptypes"
class Son extends React.Component {
state = {
sonMsg: "son message",
hasSon1: false
}
render() {
console.log("son render")
return <div>
</div>
}
}
Son.propTypes = {
msg: proptypes.string
}
Son.defaultProps = {
msg: "default"
}
export default Son;
|